A cashbook is a subsidiary book into which cash payments and cash receipts are recorded. It is a book that records the receipt and payment of money in a business firm. As cash transactions are many and entering them into the ledger immediately will make the ledger or cash account to be overloaded with irrelevant details, such transactions are first entered into the cashbook.
The cashbook is divided into three types, namely
1. The One-column cashbook
2. The two-column cashbook
3. The three-column cashbook
The One-Column Cashbook
In a small organization, cash transactions are done mainly with the use of physical cash only or by use of bank account only. Where this is the case, the cashbook in use will have only one column for amount; hence, the name One-Column Cashbook.
In a T-Form of account, the cashbook will have the debit and the credit sides. While the debit side records receipt of money, the credit side records payments of money.
Two – Column Cashbook
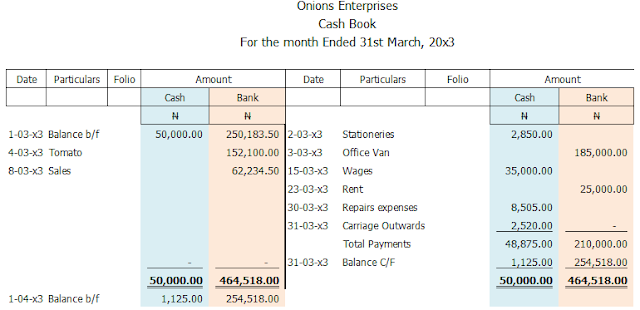
In a bigger organization where both cash and cheques are in use, we would have cash book and bank book separately. But these two books are usually merged into one called the two-column cashbook or the double column cashbook. A double column cashbook is similar to one-column cashbook. The only difference is that unlike a one-column cashbook, the double-column cashbook has two columns for amount for cash and another for amount for bank transactions.
Note
Sometimes, a transaction can appear on both the credit side and debit side of
the cash book. Such transactions are called contra entry. The implication is that
the double entries for such transactions are completed right there in the
Cashbook.
Note
The 3-Column Cashbook
A 3-column cashbook has an additional column in both sides of the cashbook.
This additional column is called the discount column. When a business firm buys
goods, it is given discount for bulk purchase or to induce quick payment. The
firm gives out discount when it sells goods to others for same purposes.
The discount a firm is given is called discount received. When it sells goods and
gives out discounts, such discounts it gives out is called discount allowed.
Discount received appears on the debit side of the cashbook while discount
allowed appears on the credit side of the cashbook.
The effects of discount is that it reduces the amount receivable or amount
payable once the criteria for the discount are met.




Comments
Post a Comment